عملية الديسك بالمنظار وعلاج الغضروف, وهو قرص مفصلي بين الفقرات بالعمود الفقري، بالفقرات العنقية والصدرية والقطنية، ويتكون من ماده غضروفيه وهلاميه ومحاطه بكبسولة قوية واقيه, ان اهتراء الغضروف وانزلاقه يأتي نتيجة حركه غير صحيحه بالفقرات، أو حمل جسم ثقيل، أو حادث أدى الى إصابة بالفقرات.
تزداد احتمالية حدوث الانزلاق الغضروفي عند المرضى نتيجة عوامل وراثيه، أو عيوب خلقيه بالفقرات، أو عيوب بالتكوين النسيجي للغضاريف ، أو مرضى الروماتيزم وأنواعه . وقد ثبت أن التدخين يؤدي الى جفاف الغضروف واهترائه مما يؤدي الى ازدياد احتمال حدوث الانزلاق الغضروفي. وأصبح التدخين من الأسباب الرئيسية للانزلاق الغضروفي
أعراض الديسك او الانزلاق الغضروفي القطني
نعني بالانزلاق الغضروفي تحرك جزء متفتت من الغضروف الى غير مكانه. وأعراض المرض تعتمد على المكان الذي انزلق اليه الجزء المتفتت من الغضروف وهذه الأعراض:
- ألم موضعي بأسفل الظهر وقد يكون محتملاً بالبداية- ويتطور الى الأسواء أو يتحسن ويكون نتيجة اهتراء الغضروف أو بروزه دون احداث ضغط على الأعصاب المغذية للأطرفة السفلى
- إذا انزلق الغضروف باتجاه مخرج العصب- المتجه الى الطرف السفلي الأيسر أو الأيمن، وتسبب بضغط على العصب القطني أو العجزي، فإنه قد يؤدي الى ألم بالطرف السفلي، وتخدر بالساق والقدم وصعوبة بالمشي. وإذا تطور الضغط على العصب فإنه قد يؤدي الى ضعف بالعصب وحركة الطرف والقدم وصعوبة بالمشي
- وإذا انزلق الغضروفي باتجاه منتصف القناة الشوكية- فإنه يؤدي الى ضغط على الجدلة العصبية كلها داخل القناة الشوكية مما يتسبب بألم بالساقين وتخدر الاليتين والساقين، وصعوبة بالمشي. وإذا تطور المرض، فإنه قد يؤدي الى فقدان السيطرة على مخارج البول والبراز، وهذه المرحلة تكون خطره بحيث تستدعي الجراحة الطارئة
علاج الديسك او الانزلاق الغضروفي
عند مراجعة المريض للطبيب المختص، والتأكد من عدم وجود ضعف بالأعصاب المغذية للأطراف السفلى أو اعصاب مخارج البول أو البراز، فإن الأولوية تكون بالعلاج التحفظي، وتشمل:
العقاقير المسكنة، والراحة، والتمارين، والسباحة، والمشي المعتدل، والعلاج الطبيعي، وقد تشمل ايضاً حقن مادة الكورتيزون بالقناة الشوكية حول الأعصاب القطنية والعجزية.
وقد تصل نسبة النجاح للسيطرة على أعراض الانزلاق الغضروفي بالعلاج التحفظي حوالي 80 %.
نلجأ الى العلاج الجراحي في الحالات التأليه:
- وجود ضعف حاد بأحد الأطراف السفلى أو كلاهما
- ضعف بالسيطرة على مخارج البول والبراز
- فشل العلاج التحفظي وعدم احتمال المريض للألم
وفي الحالتين الأوليتين، فإن الحاجة الى الجراحة تكون بصوره مستعجله وذلك لإنقاذ الأعصاب المتضررة بالسرعة الممكنة قبل حدوث الضرر الدائم.
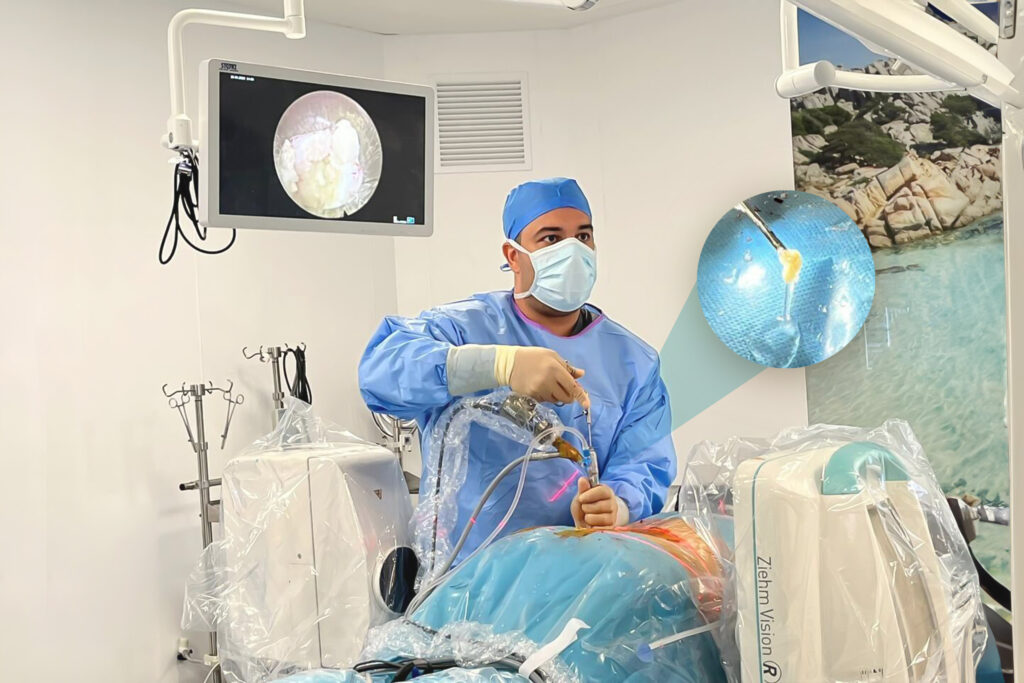
العلاج الديسك بالمنظار
تستخدم الجراحة المقننة العصبية باستخدام المنظار الخلفي لاستئصال الانزلاق الغضروفي لتلافي مخاطر القطع الكبير للأنسجة الجلدية والعضلية والعظمية كما هي بالجراحة التقليدية، وتقليل مدة الإقامة بالمستشفى، وتقليل التكلفة المادية، والإسراع بتحريك المريض من سريره بعد العملية وتتم هذه الجراحة المتطورة باستخدام:
- التخدير العام ويكون المريض بوضعيه نائم على بطنه.
- نقوم باستئصال الانزلاق الغضروفي وتوسيع مخرج العصب وبعدها نغلق الجرح الصغير
- بعد تعافي المريض من آثار العملية والتخدير، يشعر المريض باختفاء الألم بساقه، ونقوم بتحريك المريض والسماح له بالمشي باليوم التالي، ويستطيع الخروج من المستشفى وباستراحة مرضيه لمدة عدة اسابيع.
- نوصي للمريض باستخدام بعض تمارين تقوية عضلات الظهر بعد ثلاثة اسابيع من تاريخ اجراء العملية وبعدها بأسبوعين يستطيع العودة الى عمله
نسبة نجاح عملية الديسك بالمنظار
أن نسبة النجاح بالسيطرة على الألم باستخدام المنظار الخلفي لاستئصال الانزلاق الغضروفي تصل الى 95 %. وتبلغ نسبة المضاعفات حوالي 5 % وتشمل احتمالية حدوث التهاب بالجرح أو الغضروف، أو التهاب العصب، أو احتمالية اعادة المريض الى غرفة العمليات واستئصال جزء آخر من الغضروف